Ceramic Circuit Boards: The Characteristics
Due to their excellent thermal conductivity and low coefficient of thermal expansion, ceramic printed circuit boards are preferably used in the high-performance sector. In addition, the material ceramic is characterized by its excellent chemical errosion resistande and mechanical hardness.
Especially because of their extremly hardness, the materials are barely machinable with the help of mechanical cutting processes such as milling or sawing.
Application of Ceramic Circuit Boards
Ceramic printed circuit boards are used in a variety of different applications that have increased demands on robustness and reliability of the boards. These include, for example:
- Automotive industry: e.g. sensor/radar modules, ESC/ABS and EMS
- Medical technology: e.g. MEMS (Micro-Electronical-Mechanical Systems)
- Telecommunication: e.g. RF modules
- Aerospace: e.g. shockproof circuits
- Further: e.g. camera modules
Comparison of Ceramics to Further Circuit Board Materials
Laser Cutting of Ceramic PCBs
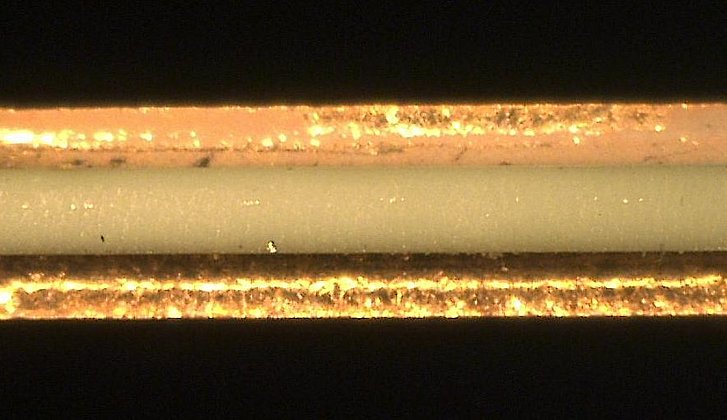
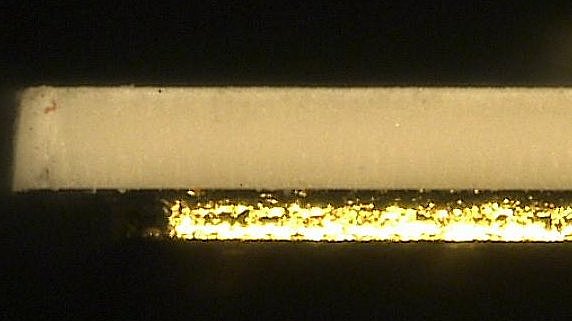
In contrast to conventional mechanical cutting processes of PCBs, laser depaneling allows ceramic materials to be processed easily and wear-free. The problem of extremely hih hardness is not a problem with non-contact ablation process of the laser.
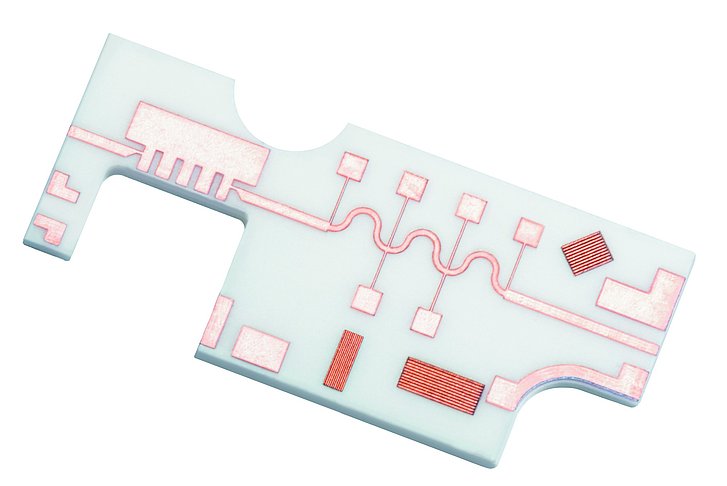
Ceramics made of aluminium oxide (see picture) can be cut technically clean at high speed even in material thicknesses of several hundred micrometers. Low (LTCC) and high (HTCC) fired ceramics can be both processed.
The laser also cuts different layouts of ceramic printed circuit boards - such as those with copper layers applied on one or both sides - technically clean and highly efficient.
The individual requirements of the different ceramic materials can be taken into account in the parameter selection of the laser processing. In this way, highly sensitive materials can be processed gently and ceramic breakage can be avoided.
Advantages of Laser Processing
Comparison to Further Separation Methods
Due to the contactless processing of the material, the laser is a completely wear-free tool. This is a major advantage, especially with regard to the above-average hardness of ceramic materials, since wearing parts such as milling heads or saw blades do not occur with the laser system. On the one hand, this directly saves costs for the components to be replaced and on the other hand, it indirectly saves costs due to avoidable downtimes of the machine.